|
Microscopy
 |
| A |
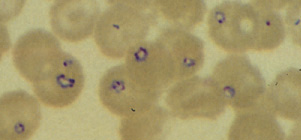
A:
Babesia microti infection, Giemsa stained thin smear. The organisms resemble
Plasmodium
falciparum; however Babesia parasites present several
distinguishing features: they vary more in shape and in size, and they do
not produce pigment. A 67-year-old woman, status postsplenectomy, infection probably acquired in Long
Island (New
York).
 |
 |
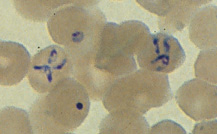
| B |
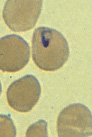
C |
B, C: Infection with Babesia.
Giemsa stained thin smears. Note in B the tetrad (left side of the
image), a dividing form pathognomonic for Babesia. Note also the variation
in size and shape of the ring stage parasites (compare B and C),
and the absence of pigment. A 6-year-old girl, status postsplenectomy for
hereditary spherocytosis, infection acquired in the United States.
|
|


