|
Microscopy
 |
 |
| A |
B |
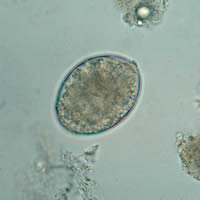
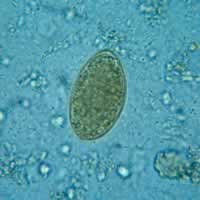
A,
B: Eggs of Diphyllobothrium latum. These eggs are oval or ellipsoidal, with an
operculum at one end that can be inconspicuous. At the
opposite (abopercular) end is a small knob that can be barely
discernible. The eggs are passed in the stool unembryonated.
Size range: 58 to 76 Ám by 40 to 51 Ám.
 |
 |
| C |
D |
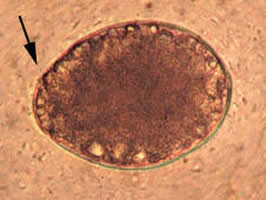
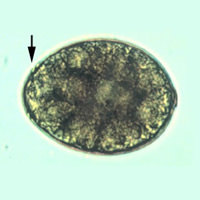
C,
D: Eggs of Diphyllobothrium latum. These eggs are oval or ellipsoidal, with an
operculum (arrows) at one end that can be inconspicuous (D). At the
opposite (abopercular) end is a small knob that can be barely discernible
(C). The eggs are passed in the stool unembryonated.
Size range: 58 to 76 Ám by 40 to 51 Ám. C: Contributed
by Georgia Division of Public Health.
 |
| E |
E:
Proglottids of Diphyllobothrium latum. These proglottids tend to be passed
in strands of variable length in the stool. The proglottids tend to be broader than
long. Image contributed by Georgia Division of Public Health.
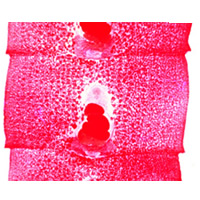 |
| F |
F: Proglottids
of Diphyllobothrium latum. The species characteristics are: the proglottid
is broader than it is long; size 2 to 4 mm long by 10 to 12 mm wide; uterus coiled in
rosette appearance; genital pore at the center of the proglottid.
|





