|
|
[Last Modified: ] |
|
|
|
| [Ancylostoma
duodenale] [Necator americanus] |
Microscopy
 |
 |
| A | B |
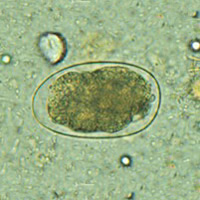
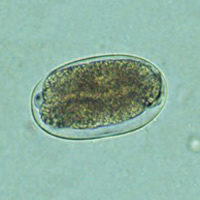
A, B: Hookworm eggs examined on wet mount (eggs of Ancylostoma duodenale and Necator americanus cannot be distinguished morphologically). Diagnostic characteristics:
- Size 57 to 76 Ám by 35 to 47 Ám
- Oval or ellipsoidal shape
- Thin shell
The embryo in B has begun cellular division and is at an early (gastrula) developmental stage.
 |
 |
| C | D |
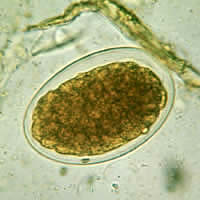
C: Hookworm
egg, advanced cleavage (iodine).
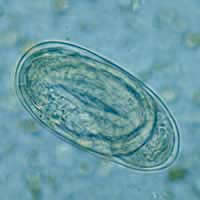
D: Embryonated hookworm egg.
 |
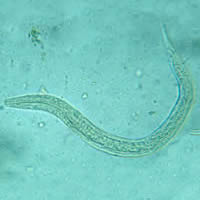 |
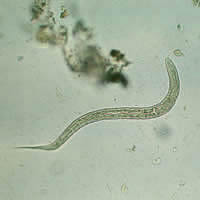
| E | F |
E, F: Hookworm rhabditiform larva (wet preparation).
 |
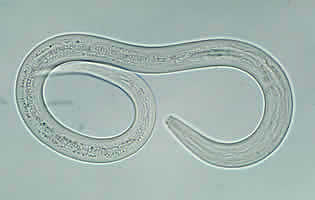 |
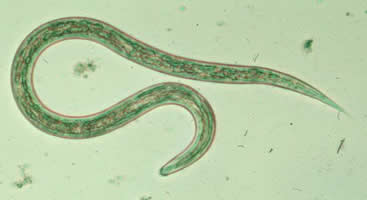
| G | H |
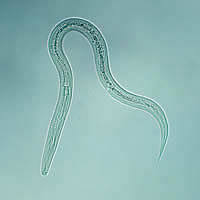
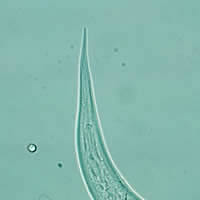
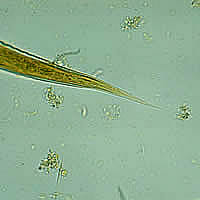
G, H: Hookworm filariform larva (wet preparation).
 |
 |
 |
| I | J | K |
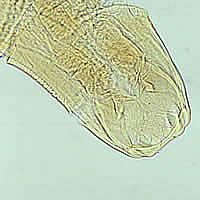
I, J, K: Hookworm filariform larva (I and J, wet preparations; K, iodine). Larva tail is depicted in Figures J and K.
 |
 |
| L | M |
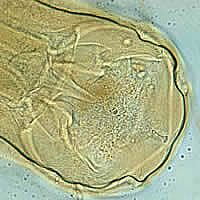
L:
Adult
worm of Ancylostoma duodenale. Anterior end is depicted showing
cutting teeth.
M: Adult worm of Necator americanus.
Anterior
end showing mouth parts with cutting plates.
|
|||