|
|
[Last Modified: ] |
 |
|
| [Pneumocystis jiroveci] |
Causal Agent:
Pneumocystis
jiroveci (previously classified as Pneumocystis carinii)
was previously classified as a protozoa. Currently, it is considered a
fungus based on nucleic acid and biochemical analysis.
Reference:
- Frenkel JK. Pneumocystis pneumonia, an immunodeficiency-dependent disease (IDD): a critical historical overview. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1999;46:89S–92S.
- Stringer JR, Beard CB, Miller RF, Wakefield, AE. A New Name (Pneumocystis jiroveci) for Pneumocystis from Humans. Emerg Infect Dis 2002;8:891-896.
Pneumocystis stages were reproduced
from a drawing by Dr. John J. Ruffolo, South
Dakota State University, USA published in Cushion M. Pneumocystis
carinii. In: Collier L, Balows A, Sussman M, editors. Topley and
Wilson's Microbiology and Microbial Infections: Volume 4 Medical Mycology,
9th ed. New York: Arnold Publishing; 1998. p. 674. Copyright held by Arnold Publishing
and reproduced here by permission of Arnold and
Dr. Ruffolo.
Our thanks to Dr. Melanie T. Cushion for her comments
on the life cycle text.
References:
- Ruffolo JJ. Pneumocystis carinii Cell Structure. In: Walzer, PD, editor. Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia. 2nd ed. Marcel Dekker; 1994. p. 25-43.
- Cushion MT, Ruffolo JJ, Walzer PD. Analysis of the developmental stages of Pneumocystis carinii in vitro. Lab Invest 1988;58:324-331.
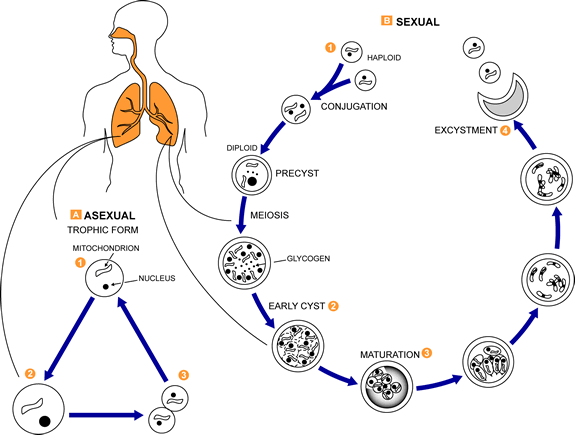
This is a
generalized life cycle proposed by John J. Ruffolo, Ph.D.
(Cushion, MT, 1988) for the various species of Pneumocystis. These fungi are found in the lungs of mammals where
they reside without causing overt infection until the host's immune system
becomes debilitated. Then, an oftentimes lethal pneumonia can result. Asexual phase: trophic forms
![]() replicate by mitosis
replicate by mitosis
![]() to
to
![]() .
Sexual phase: haploid trophic forms conjugate
.
Sexual phase: haploid trophic forms conjugate
![]() and produce a zygote or sporocyte (early cyst)
and produce a zygote or sporocyte (early cyst)
![]() .
The zygote undergoes meiosis and subsequent mitosis to produce eight
haploid nuclei (late phase cyst)
.
The zygote undergoes meiosis and subsequent mitosis to produce eight
haploid nuclei (late phase cyst)
![]() .
Spores exhibit different shapes (such as, spherical and elongated forms).
It is postulated that elongation of the spores precedes release from the
spore case. It is believed that the release occurs through a rent in
the cell wall. After release, the empty spore case usually collapses,
but retains some residual cytoplasm
.
Spores exhibit different shapes (such as, spherical and elongated forms).
It is postulated that elongation of the spores precedes release from the
spore case. It is believed that the release occurs through a rent in
the cell wall. After release, the empty spore case usually collapses,
but retains some residual cytoplasm
![]() .
A trophic stage, where the organisms probably multiply by binary fission
is also recognized to exist. The organism causes disease
in immunosuppressed individuals.
.
A trophic stage, where the organisms probably multiply by binary fission
is also recognized to exist. The organism causes disease
in immunosuppressed individuals.
Geographic
Distribution:
Worldwide, in humans
and animals. Serologic evidence indicates that most healthy children have been
exposed by age 3 to 4. Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) occurs in
immunosuppressed individuals and in premature, malnourished infants.
|
||||||||