|
|
[Last Modified: ] |
|
|
|
| [Entamoeba histolytica] |
Molecular
diagnosis
In reference diagnosis
laboratories, PCR is the method of choice for discriminating between the pathogenic
species (E. histolytica) from the nonpathogenic species (E. dispar).
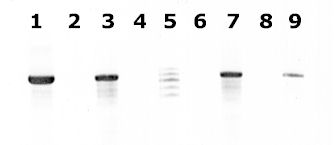 |
| A |
A: Agarose gel (2%) analysis of a PCR diagnostic test for differentiation between E. histolytica and E. dispar.
- Lanes 1 - 4: Amplification with the Psp3/Psp51 PCR primer pair specific for E. histolytica. Diagnostic band size - 876 bp.
- Lanes 6 - 9: Amplification with the NPsp3/NPsp51 PCR primer pair specific for E. dispar. Diagnostic band size - 876 bp.
- Lanes 1 and 6: E. histolytica 200:NIH, zymodeme II (positive control for E. histolytica).
- Lanes 2 and 7: E. dispar 351:IMMiT, zymodeme I (positive control for E. dispar).
- Lanes 3 and 8: Specimen from a patient with a liver abscess (positive with E. histolytica primers and negative with E. dispar primers). E. histolytica 333:IMMiT, zymodeme XIV.
- Lanes 4 and 9: Specimen from an asymptomatic patient (positive with E. dispar primers and negative with with E. histolytica primers). E. dispar 389:IMMiT, zymodeme I.
- Lane 5: Molecular base pair standard, 100-bp ladder (from 600 to 1,000 bp).
Figure contributed by Assist. Prof. Przemyslaw Myjak, Ph.D., Institute of Maritime and Tropical Medicine, Gdynia, Poland.
Reference:
Clark CG, Diamond LS. Differentiation of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica from other intestinal protozoa by riboprinting. Arch Med Res 1992;23:15-16.
|
|||