|
Molecular
Diagnosis
Molecular methods for
detection of P. jiroveci have shown very high sensitivity and specificity and
constitute the gold standard for detection of this pathogen.
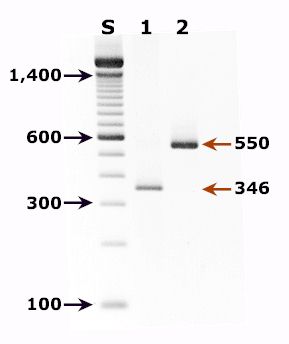 |
| A |
A: Agarose gel
(2%) analysis of PCR-amplified products from DNA extracted from a bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) diagnostic
specimen of a patient with pulmonary symptoms.
- Lane S: Molecular base
pair standard (100-bp ladder). Black arrows show the size of standard bands.
- Lane 1: Single-step PCR
amplification with the pAZ102-E/pAZ102-H primer pair1 - diagnostic band size:
346 bp.
- Lane 2: Nested PCR
amplification with the ITS nested PCR primers, 1724F/ITS2R (first round) and ITS1F/ITS2R1
(second round)2 - diagnostic band size: 550 bp.
References:
- Wakefield AE, Pixley FJ, Banerji S, Sinclair K, Miller RF, Moxon ER, Hopkin JM.
Amplification of mitochondrial ribosomal RNA sequences from Pneumocystis carinii of
rat and human origin. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1990;43:69-76.
- Lu JJ, Chen CH, Bartlett MS, Smith JW, Lee CH. Comparison of six different PCR methods
for detection of Pneumocystis carinii. J Clin Microbiol 1995;33:2785-2788.
|
|

