|
|
[Last Modified: ] |
|
|
|
| [Schistosoma
mansoni] [Schistosoma haematobium] [Schistosoma japonicum] [Schistosoma mekongi] [Schistosoma intercalatum] |
Microscopy
Schistosoma mansoni
 |
 |
| A | B |
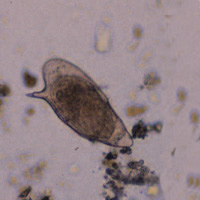
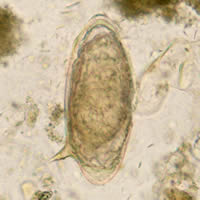
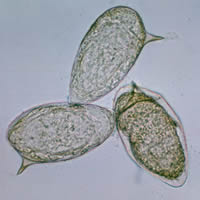
A, B: Schistosoma mansoni eggs in a patient from Egypt. These eggs are large (length 114 to 180 Ám) and have a characteristic shape, with a prominent lateral spine near the posterior end. The anterior end is tapered and slightly curved. When the eggs are excreted, they contain a mature miracidium (especially visible in A).
 |
 |
| C | D |
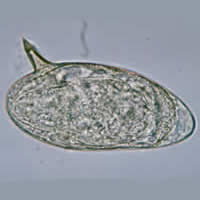
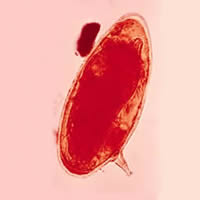
C, D: Schistosoma mansoni eggs showing characteristic lateral spine.
 |
 |
 |
| E | F | G |
E: Schistosoma
mansoni egg (iodine stain).
F: Schistosoma mansoni eggs
(wet preparation).
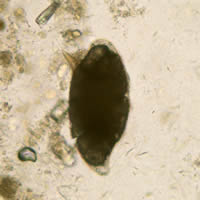
G: Nonviable Schistosoma mansoni egg.
Schistosoma japonicum
 |
 |
| H | I |
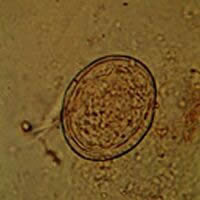
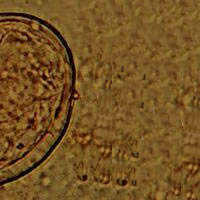
H, I: Schistosoma japonicum egg. The egg is typically oval and has a vestigial spine, which is better shown in Figure I. Schistosoma japonicum eggs are smaller (68 to 100 Ám by 45 to 80 Ám) than those of the other species.
 |
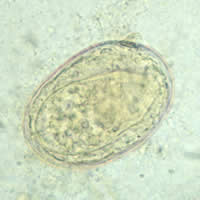 |
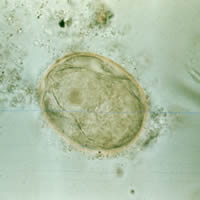
| J | K |
 |
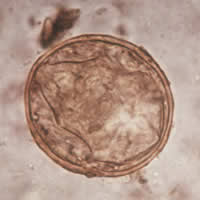 |
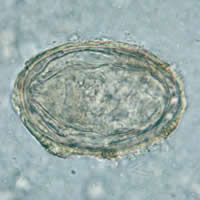
| L | M |
J, K, L, M: Schistosoma japonicum eggs. In Figures J, K, and L the spine is not distinct. The egg in Figure M shows a visible spine.
|
||||||||